Magnesium citrate stands out as a highly bioavailable form of magnesium that supports multiple bodily functions. This comprehensive guide explores how this essential mineral contributes to bone health, muscle function, sleep quality, and digestive regularity while comparing it with other popular forms.
What Is Magnesium Citrate?
Magnesium citrate combines magnesium with citric acid, creating a highly absorbable supplement form that efficiently delivers this essential mineral to your body. Many health professionals recommend magnesium citrate for its superior bioavailability compared to other magnesium supplements.
The human body requires magnesium for over 300 biochemical reactions. This mineral plays a vital role in energy production, protein synthesis, muscle movement, nervous system regulation, and maintaining healthy bones and teeth.
Unfortunately, many people don’t consume enough magnesium through their diet alone. Modern farming practices and food processing methods have reduced the magnesium content in many foods, making supplementation increasingly important for optimal health.
Key Magnesium Citrate Benefits
Magnesium citrate offers numerous health advantages that support overall wellbeing. Understanding these benefits helps you make informed decisions about incorporating this supplement into your health regimen.
Supports Muscle Function
Magnesium citrate helps maintain proper muscle contraction and relaxation. This function proves especially beneficial for those experiencing muscle cramps, spasms, or tension. Athletes and physically active individuals often use magnesium supplements to support muscle recovery and prevent post-exercise soreness.
Promotes Bone Health
This mineral works synergistically with calcium and vitamin D to build and maintain strong bones. Magnesium helps regulate calcium transport and absorption, thereby supporting bone density and reducing osteoporosis risk. Regular magnesium intake contributes significantly to long-term skeletal health.
Enhances Nervous System Function
Magnesium citrate supports healthy nerve transmission and neurotransmitter activity. This function helps regulate mood and stress responses while potentially alleviating symptoms of anxiety. The calming effect on the nervous system makes magnesium particularly valuable during periods of heightened stress.
Reduces Fatigue
Feeling constantly tired? Magnesium citrate may help. This mineral plays a crucial role in energy production at the cellular level. Adequate magnesium levels support ATP (adenosine triphosphate) production – your body’s primary energy currency – helping combat fatigue and low energy.
Supports Psychological Function
Research suggests magnesium contributes to normal psychological function and cognitive performance. Some studies indicate that magnesium supplementation may help manage symptoms of depression and anxiety, though more research continues in this area.
Maintains Electrolyte Balance
Magnesium functions as an electrolyte in the body, helping regulate fluid balance and supporting proper nerve and muscle function. This electrolyte balance proves particularly important during intense physical activity or periods of illness when electrolyte levels may fluctuate.
Magnesium Citrate for Sleep
Many people struggle with sleep difficulties, making natural solutions increasingly valuable. Magnesium citrate has gained popularity as a natural sleep aid due to its relaxing properties.
This mineral helps activate the parasympathetic nervous system responsible for relaxation and promotes the production of melatonin, your body’s sleep hormone. Additionally, magnesium regulates GABA receptors in the brain, which help calm nervous system activity.
Taking magnesium citrate before bedtime may help reduce the time needed to fall asleep and improve overall sleep quality. Many users report experiencing deeper, more restorative sleep after incorporating this supplement into their evening routine.
Magnesium Citrate for Constipation
One well-known application of magnesium citrate involves its effectiveness as a gentle laxative. This benefit results from magnesium’s ability to draw water into the intestines, softening stool and promoting bowel movements.
Healthcare professionals often recommend magnesium citrate for occasional constipation relief. The supplement typically works within 30 minutes to 6 hours, making it relatively fast-acting compared to other natural constipation remedies.
However, this effect varies between individuals based on dosage and personal sensitivity. Start with a lower dose if using magnesium specifically for digestive purposes, gradually increasing as needed while monitoring your body’s response.
Magnesium Citrate vs Glycinate: Which Should You Choose?
When selecting a magnesium supplement, many people find themselves deciding between magnesium citrate and magnesium glycinate. Both offer excellent bioavailability, but they serve slightly different purposes.
Vitamins & Minerals
Magnesium Glycinate 1800mg Complex 90 Capsules by Nutrition Geeks
Experience the benefits of our Magnesium Glycinate 3-in-1 Complex, featuring 1800mg of magnesium compounds in a highly absorbable formula. This vegan-friendly supplement supports muscle relaxation, energy levels, and overall well-being. Each pack contains 90 capsules, providing a convenient and sustainable solution for your daily magnesium needs.
Vitamins & Minerals
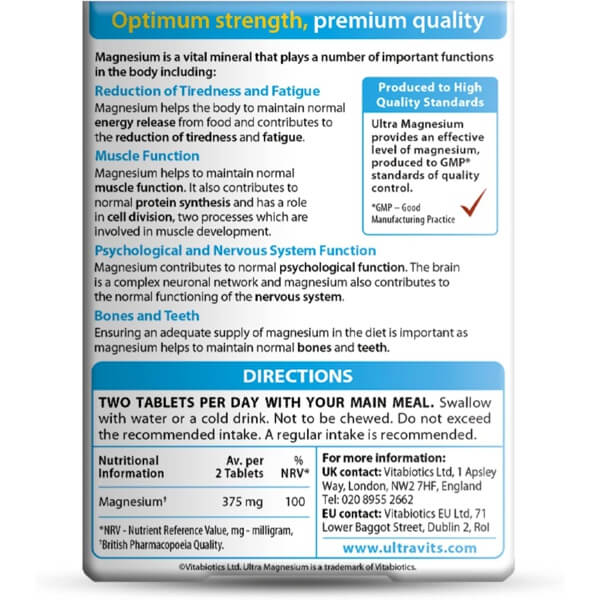
Magnesium Ultra 375mg Premium Supplement 60 Tablets by Vitabiotics
Magnesium plays a number of important roles within the body including helping to maintain normal bones and teeth. Mineral contributes to normal functioning of the nervous system and has a role in the process of cell division. The presence of the mineral magnesium, as well as contributing to the maintenance of normal bones and teeth, also contributes to normal protein synthesis and electrolyte balance.
Absorption and Bioavailability
Both magnesium citrate and magnesium glycinate demonstrate good absorption rates. Magnesium citrate combines magnesium with citric acid, creating a compound that dissolves easily in water. Magnesium glycinate binds magnesium to the amino acid glycine, which facilitates absorption through the intestinal wall.
Digestive Effects
The most significant difference between these supplements involves their effects on digestion. Magnesium citrate has mild laxative properties that can help relieve constipation but might cause digestive discomfort at higher doses.
Magnesium glycinate, conversely, typically causes minimal digestive disturbance. This gentle profile makes glycinate particularly suitable for those with sensitive digestive systems or inflammatory bowel conditions.
Sleep Support
While both forms can support sleep, magnesium glycinate often receives preference for sleep-specific concerns. The glycine component has its own calming, sleep-promoting properties that complement magnesium’s relaxation effects.
However, magnesium citrate remains effective for sleep support as well, especially when poor sleep relates to muscle tension or stress.
Muscle Recovery
Athletes and physically active individuals might benefit from either form. Magnesium citrate works well for those needing both muscle support and improved digestion. Magnesium glycinate provides muscle benefits without the laxative effect, making it suitable for use before physical activity.
The best choice ultimately depends on your specific health needs, digestive sensitivity, and intended use. Some people even alternate between both forms to gain their respective benefits.
Potential Magnesium Side Effects
While magnesium citrate offers numerous health benefits, being aware of potential side effects helps ensure safe supplementation. Most healthy individuals tolerate magnesium citrate well when taken as directed, but some may experience:
Digestive Discomfort
The most common side effects involve the digestive system. Some people may experience diarrhea, abdominal cramping, or nausea, particularly at higher doses. These effects typically result from magnesium’s natural osmotic action in the intestines.
Electrolyte Imbalances
Excessive magnesium supplementation may potentially disrupt your body’s mineral balance. This imbalance could affect calcium, potassium, and sodium levels, though this rarely occurs with standard supplemental doses.
Drug Interactions
Magnesium citrate might interact with certain medications, including antibiotics, bisphosphonates, and some heart medications. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting magnesium supplementation if you take prescription medications.
Hypotension
In some sensitive individuals, magnesium may lower blood pressure. People with already low blood pressure should monitor their response when beginning supplementation.
To minimize potential side effects, start with a lower dose and gradually increase as tolerated. Taking magnesium citrate with food can also help reduce digestive discomfort.
Choosing Quality Magnesium Supplements
Not all magnesium supplements offer equal quality and efficacy. When selecting a magnesium citrate product, consider these important factors:
Elemental Magnesium Content
Check the elemental magnesium content rather than just the total compound weight. A quality supplement clearly states the amount of actual magnesium provided per serving, typically between 200-400mg of elemental magnesium daily for most adults.
Third-Party Testing
Choose products tested by independent laboratories for purity and potency. These tests verify that supplements contain the advertised ingredients without harmful contaminants like heavy metals or microbiological impurities.
Manufacturing Standards
Look for supplements produced in facilities following Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). This certification ensures adherence to strict quality control standards throughout the production process.
Additives and Fillers
Minimize unnecessary ingredients by selecting supplements with minimal additives, fillers, or artificial compounds. Vegans and those with dietary restrictions should verify capsule materials and avoid products containing animal-derived ingredients.
Recommended Dosage and Usage Instructions
Follow dosage guidelines provided by the manufacturer or your healthcare provider. Most adults benefit from 200-400mg of elemental magnesium daily, divided into 1-2 doses. Taking magnesium citrate with meals often improves absorption and reduces potential digestive discomfort.